Für Einsteiger ist SeaTables Terminologie nicht ganz einfach: Was ist eine Base? Was ist der Unterschied zwischen einem Team und einer Gruppe? Was hat es mit einer Ansicht auf sich und wo befinden sich die Ansichtsoptionen? In diesem Glossar erläutern wir die für SeaTable zentralen Begriffe und Konzepte und setzen sie miteinander in Beziehung. Für eine einfache Nachvollziehbarkeit erfolgt dies anhand der unterschiedlichen Elemente der SeaTable Benutzeroberfläche.
Startseite
| Begriff | Erklärung oder Beschreibung |
|---|---|
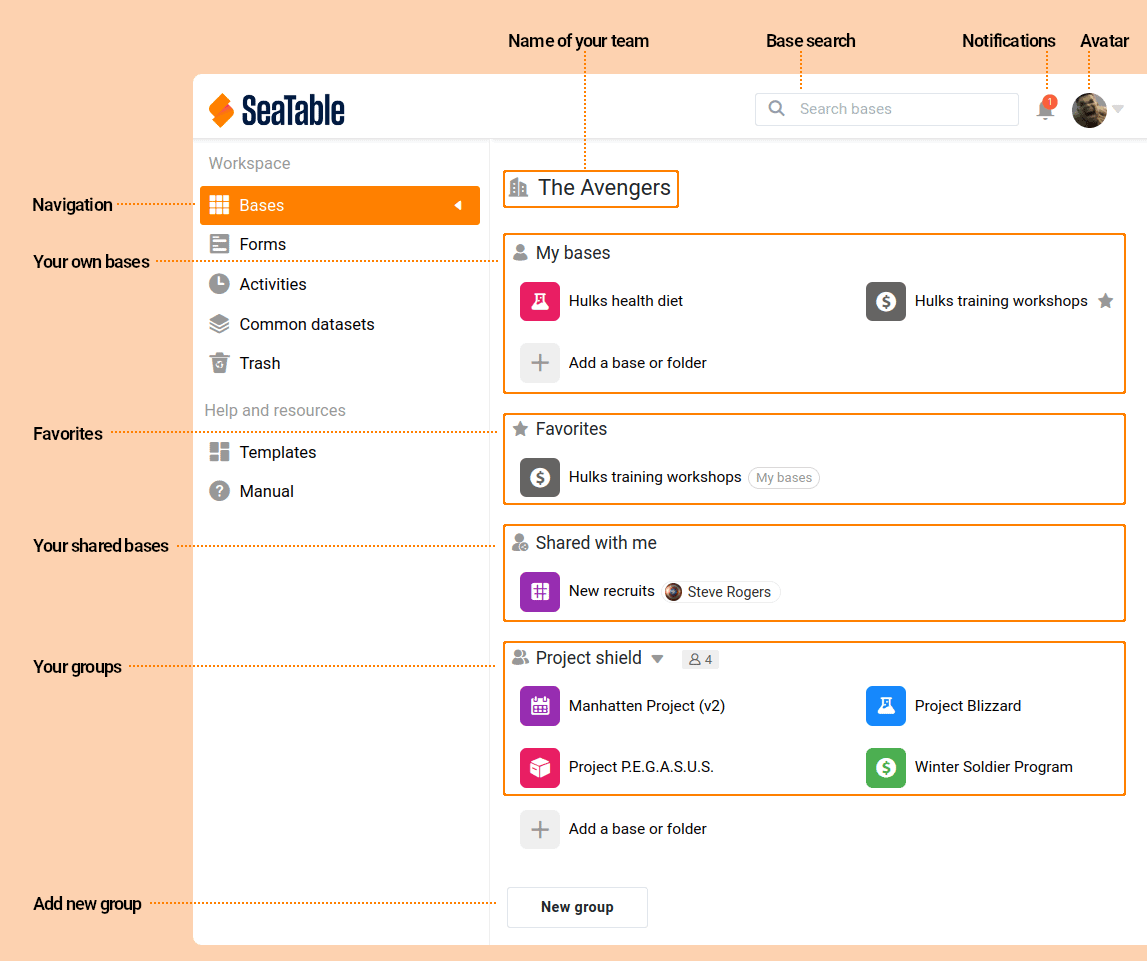
| Startseite 🇬🇧 home page | Die Startseite erscheint nach der Anmeldung in SeaTable. Sie hat zwei Hauptelemente: Die Navigation (links) und die Übersicht der Bases (rechts). |
| Team 🇬🇧 team (nur SeaTable Cloud) | Ein Team setzt sich aus allen Benutzern eines SeaTable Cloud Abonnements zusammen. Ein Teammitglied kann eine Base direkt an ein anderes Teammitglied freigeben. Teammitglieder können auch Gruppen formen. Die Verwaltung eines Teams erfolgt in der Teamverwaltung durch einen oder mehrere Teamadministratoren. Die Teamverwaltung kann durch einen Klick auf den Avatar aufgerufen werden. Ein Teamadministrator kann auch Anpassungen am SeaTable Cloud Abonnement vornehmen. |
| Gruppe 🇬🇧 group | Eine Gruppe besteht aus einem oder mehreren Teammitgliedern. Eine Gruppe ist somit ein Mittel, um Benutzer innerhalb eines Teams thematisch zu ordnen und einfach zusammenarbeiten zu lassen. Jede Gruppe wird über ihren Namen im Team eindeutig identifiziert. Jedem Gruppenmitglied ist eine Rolle zugeordnet, die die Berechtigungen des Benutzers in der Gruppe definiert. Unabhängig von der Rolle kann jedes Gruppenmitglied auf alle Bases der Gruppe zugreifen. |
| Base 🇬🇧 base | Eine Base ist eine Datenbank. Eine Base besteht aus einer oder mehreren Tabellen und kann viele Tausend Zeilen enthalten. Alle Bases, auf die ein Benutzer Zugriff hat, werden auf der Startseite angezeigt. Aus Benutzerperspektive gibt es drei Arten von Bases: Meine Bases (englisch "My bases") wurden vom Benutzer erstellt und gehören dem Benutzer. Geteilte bzw. freigegebene Bases (englisch "shared bases") sind im Besitz eines anderen Benutzers, wurden von diesem aber an Sie freigegeben, so dass Sie auch auf die Daten zugreifen können. Gruppenbases (englisch "group bases") sind Bases, die innerhalb einer Gruppe erstellt wurden und daher der Gruppe gehören. |
| Favoriten 🇬🇧 favorites | Die Favoriten sind häufig verwendete Bases eines Benutzers. Sie werden auf der Startseite in einem separaten Bereich angezeigt. Ein Benutzer kann selbst Bases zu seinen Favoriten hinzufügen und aus diesen auch wieder entfernen. |
| Vorlage 🇬🇧 template | Eine Vorlage ist eine Base mit einer für einen bestimmten Anwendungsfall vorgefertigten Tabellen- und Datenstruktur. Eine Vorlage bietet somit eine Abkürzung zur Entwicklung einer Anwendung in SeaTable. |
| Benachrichtigung 🇬🇧 notification | Eine Benachrichtigung ist eine Mitteilung innerhalb von SeaTable. Eine Benachrichtigung kann vom System erstellt werden (z. B. wenn ein Benutzer mit einem anderen eine Base teilt) oder durch Benutzer aktiv versendet werden (z. B. durch eine Schaltflächenaktion oder einen Zeilenkommentar). Wenn neue Benachrichtigungen vorliegen, dann wird dies durch eine Zahl am Glocken-Icon angezeigt. |
| Avatar 🇬🇧 avatar | Der Avatar ist die Abbildung, die einem Benutzer in SeaTable zugeordnet ist. Der Avatar wird an vielen Stellen in SeaTable verwendet, um den Benutzer zu repräsentieren (z. B. in den Logs). Benutzer können ihren Avatar selbst auswählen und ändern. |
Base
| Begriff | Erklärung oder Beschreibung |
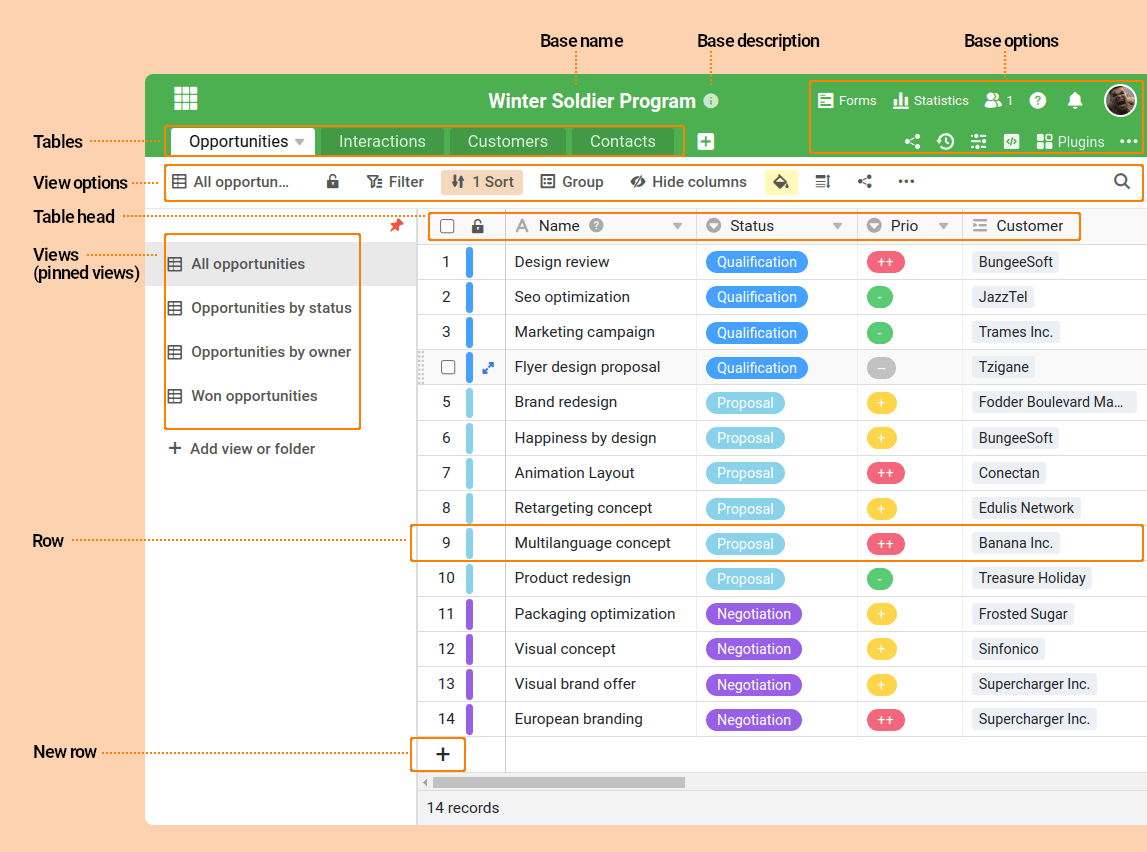
| Tabelle 🇬🇧 table | Tabellen sind die konstitutiven Elemente von Bases. Eine Tabelle besteht aus Spalten, Zeilen und Ansichten. Jede Tabelle wird in einer Base als Registerkarte angezeigt. Zwischen Tabellen in SeaTable und in Tabellenkalkulationen (z.B. Excel) gibt es einen fundamentalen Unterschied: In SeaTable lassen sich zwischen Datensätzen Verknüpfungen erstellen. Dies macht eine Base in SeaTable zu einer relationalen Datenbank. In Tabellenkalkulationen können Sie nur andere Zellen referenzieren. |
| Ansicht 🇬🇧 view | Eine Ansicht ist eine benutzerdefinierte Darstellung der Daten in einer Tabelle. Eine Ansicht wird durch die genutzten Sortierungen, Filter, Gruppierungen, Spaltenausblendungen sowie weitere Ansichtseinstellungen definiert. Eine Tabelle kann eine oder mehrere Ansichten enthalten. Alle Ansichten einer Tabelle greifen auf den gleichen Datenbestand zu. Das bedeutet: Wird ein Zellenwert in einer Ansicht geändert, dann wird der Wert in der zugrundeliegenden Tabelle geändert und damit auch in allen Ansichten der Tabelle. Wird eine Ansicht gesperrt, lassen sich die Ansichtseinstellungen nicht mehr ändern. |
| Tabellenkopf 🇬🇧 table header | Der Tabellenkopf enthält alle Spaltenüberschriften einer Tabelle sowie deren Metainformationen (z.B. Spaltentyp, Spaltenbeschreibung, Spaltenbreite). Wird der Tabellenkopf gesperrt, lassen sich alle Elemente des Tabellenkopfs nicht mehr ändern. |
| Spalte 🇬🇧 column | Eine Spalte erfasst Daten eines Typs. SeaTable bietet 25 unterschiedliche Spaltentypen, um so unterschiedliche Informationen wie Text, Datum, Zahlen, Bilder, Dateien, Checkboxen oder Formeln speichern zu können. Die erste Spalte in jeder Tabelle kann nicht gelöscht, verschoben oder ausgeblendet werden. Auch stehen in der ersten Spalte nur 6 Spaltentypen zur Verfügung. |
| Zeile 🇬🇧 row | Eine Zeile stellt einen Datensatz dar. |
| Plugins 🇬🇧 plugins | Plugins sind Erweiterungen für SeaTable. Es gibt unterschiedliche Arten von Plugins. Plugins für die Datenvisualisierung sind die Galerie, der Kalender, die Karte, das Kanban- und das Timeline-Plugin. Das Seitendesign-Plugin ist ein Plugin, das die Gestaltung von Dokumenten ermöglicht. Mit der SQL-Abfrage und der Datendeduplizierung können Sie Datensätze suchen und löschen. Plugins lassen sich auch individuell entwickeln. |
| Zeilendetails 🇬🇧 row details | Die Zeilendetails stellen alle (nicht ausgeblendeten) Spalten eines Datensatzes auf einer Seite dar. Schreibgeschützte Spalten sind durch einen grauen Hintergrund gekennzeichnet; alle anderen Spalten können Sie bearbeiten. In den Zeilendetails werden auch die Kommentare und die Bearbeitungshistorie des Datensatzes (soweit verfügbar) angezeigt. |
| Basebeschreibung 🇬🇧 base description | Jede Base verfügt über eine Basebeschreibung, die automatisch geöffnet wird, wenn ein Benutzer die Base das erste Mal öffnet. Eine Beschreibung eignet sich dafür, Benutzern eine Gebrauchsanweisung oder zusätzliche Informationen zu einer Base zur Verfügung zu stellen. |
| Ansichtsoptionen 🇬🇧 view options | Die Ansichtsoptionen umfassen sämtliche Einstellungen und Funktionen, mit denen Ansichten erstellt, modifiziert und verwaltet werden können. |
| Formulare 🇬🇧 forms | Ein Formular ist eine Webseite, über die neue Datensätze angelegt werden können. SeaTable Formulare sind standardmäßig öffentlich, können aber auch zugriffsbeschränkt werden. |
| App 🇬🇧 app | Eine SeaTable App ist eine Webanwendung mit eigenem Namen und eigener URL, die auf einer Base basiert. Da eine Base mehrere Apps unterstützt, lassen sich mit Apps spezifische Webanwendungen entwickeln, die für ihre jeweilige Benutzerzielgruppe optimiert sind. |
| Statistik 🇬🇧 statistic | Eine Statistik ist eine quantitative Auswertung des Inhalts einer Tabelle. SeaTable stellt diverse (einfache und kombinierte) Diagrammtypen und Pivot-Tabellen als Statistiken zur Verfügung. |
| Automation 🇬🇧 automation | Eine Automation ist eine Abfolge von definierten Aktionen, die ausgeführt werden, wenn ein bestimmtes Ereignis eintritt und/oder eine bestimmte Bedingung erfüllt ist. Automationen können wiederkehrende Aufgaben zuverlässig erledigen und dadurch Zeitaufwand und Fehler minimieren. |
| Skript 🇬🇧 script | Skripte sind kleine Programme, um wiederkehrende oder aufwändige Datenverarbeitungsprozesse zu automatisieren. SeaTable kann Skripte in JavaScript und Python verarbeiten. Skripte können entweder manuell durch eine Schaltfläche oder eine Automation ausgelöst werden. |
| Freigabe 🇬🇧 share | Eine Freigabe ist die Erlaubnis eines Benutzers an einen anderen Benutzer, auf eine Ressource zuzugreifen. Freigaben können in SeaTable für eine gesamte Base, Teile einer Base oder eine einzelne Ansicht erteilt werden. Das Berechtigungsniveau der Freigabe definiert, welchen Zugriff der Benutzer auf die Daten hat (nur lesen oder auch bearbeiten). |